Senior AWS Consultant
Nobody cares about backups – restores, on the other hand…
Backup is like insurance – nice to have, but ideally, you’ll never need it. That being said, like insurance, it should be tailored to your specific business needs. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution.
Everyone wants their specific requirements taken into account when designing a backup strategy – first and foremost the business, followed by IT operations, IT security, IT platform teams, FinOps, and sometimes even regulators. The latter applies only to highly regulated industries.
Backup strategies should be aligned with the needs of the business, as backups contribute to overall business continuity. Of course, other factors are also important, including:
- Security of backups and access control
- Ease of operations
- Overall costs, including licensing and staffing
- Deployment and maintainability
Most products available today check most, if not all, of these boxes in terms of features, allowing customers to choose from a wide variety of backup solutions.
For greenfield customers or those who can’t yet move their current backup solution to the cloud, AWS Backup may be an interesting option.
AWS Backup
As a managed service, AWS Backup offers several key benefits. It requires zero maintenance, follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, and leverages everything AWS offers in terms of security and access management. This includes encryption at rest via AWS Key Management Service (KMS), with support for customer-managed keys, as well as a full spectrum of identity- and resource-based policies to secure access to backup vaults.
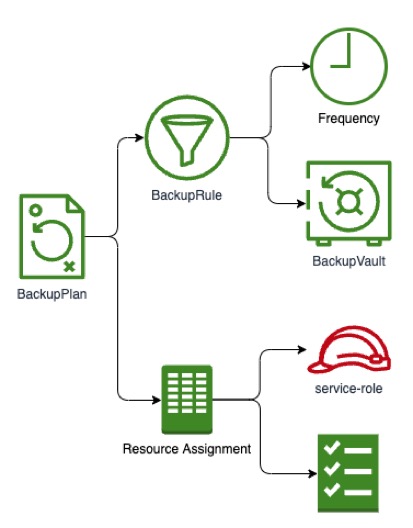
In addition to manual backups, AWS Backup allows users to create automated backups using Backup Plans that define which resources are included through Backup Selections. It’s also possible to create custom automations with these mechanisms, enabling event-driven backups rather than just scheduled ones.
When a backup is initiated, AWS Backup uses a service role to trigger the service-specific mechanism that creates a copy of the resource or object. This could be an EC2 AMI, EBS snapshot, S3 version, RDS snapshot, and so on. Once successfully created, the backup is stored in the Backup Vault, where it remains secure, immutable, and frozen.
Thanks to this design, backup vaults are never directly accessed by other services or principals. They remain completely isolated from the application’s local network and can only be accessed with explicit permissions.
Technical overview
From a technical standpoint, AWS Backup Vaults likely use a technology similar to Amazon S3, given the overlapping feature set. For example, Vault Lock options function exactly like S3 Object Lock, and backups can be moved to colder storage tiers.
AWS Backup consists of several key components that work together:
- Backup Vault
- Stores backups in an isolated, write-once-read-many (WORM), and encrypted environment, protected by Vault Access Policies.
- Backup Plan
- Defines schedules, time windows, and target vaults for backups. Copy actions to additional vaults can also be configured.
- Backup Selection
- Determines which resources are backed up within a given Backup Plan. Multiple selections can be part of the same plan for greater flexibility.
Ransomware
While ransomware threats seem to be ubiquitous, AWS Backup provides a vault solution to protect your backups from deletion and encryption. This doesn’t mean that AWS Backup will magically protect your applications from ransomware, but it can be an important part of the solution to protect your workloads from ransomware and further improve your security posture against potential threats.
Air-gapping your backup strategies
Creating a complete backup strategy from scratch can be challenging – especially in regulated environments where business requirements can be difficult to meet.
This is where AWS Backup’s flexibility shines. By creating multiple Backup Plans with resource-specific selections, organizations can ensure that different workloads are backed up according to their specific needs. Additionally, AWS Backup supports continuous backups for RDS and S3, reducing the gap between recovery points to zero.
The cherry on top? The ability to create event-driven backups using AWS Lambda or scripts via the AWS CLI. This allows backups to be triggered based on specific events or metrics, rather than being confined to a schedule.